The glass condenser tube is an instrument that takes advantage of the principle of heat exchange to make cool and condense gas into liquid. It is usually composed of two glass tubes, one inside and one outside, in which the smaller glass tube runs through, the larger glass tube. Both ends of the inner tube of the condensing tube are provided with a connecting port, which can be connected with other equipment of the experimental device to allow the hotter gas or liquid to condense through the inner tube. The outer pipe usually has an up-and-down opening on both sides to connect the plastic pipe carrying cooling substances (such as water). When in use, the lower opening of the outer tube can be connected to the faucet because the water will automatically flow upward in case of heat in the condensing pipe to achieve a more significant cooling effect.
Material: High borosilicate glass.
In total, there are three kinds of glass condenser tubes:
1. Spiral Shaped

The spiral-shaped glass condenser tube is used to reflux organic preparation, which is more suitable for liquid with a low boiling point. The inner tube is spiral-shaped, increasing the length and expanding the condensation area. Steam can be cooled by air and water at the same time.
2. Straight Shaped

The straight-shaped glass condensing tube is suitable for distilling and fractionating substances with a boiling point below 140 ℃. It is mainly used in inclined distillation units and is unsuitable for reflux. The inner tube of the straight condenser tube is a straight glass tube.
3. Spherical Shaped
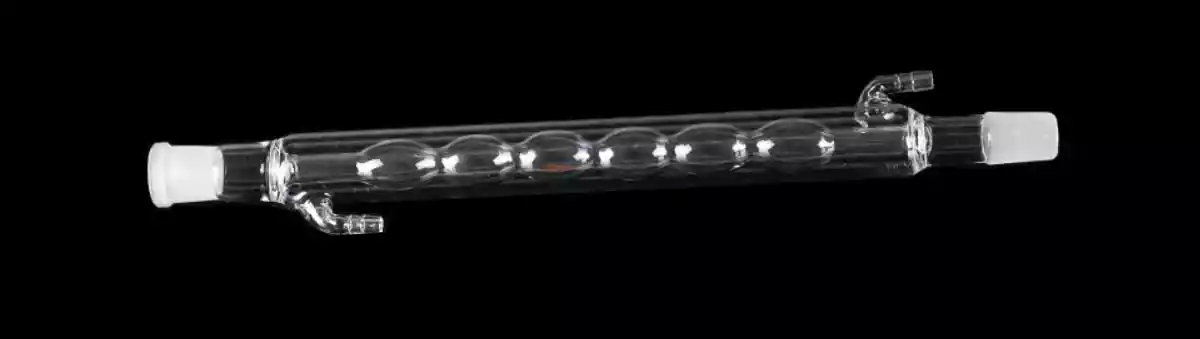
The spherical-shaped glass condenser tube is used to reflux organic preparation and is suitable for liquids with various boiling points. The inner tube of the glass condenser tube is several connected glass balls.
Size Details:
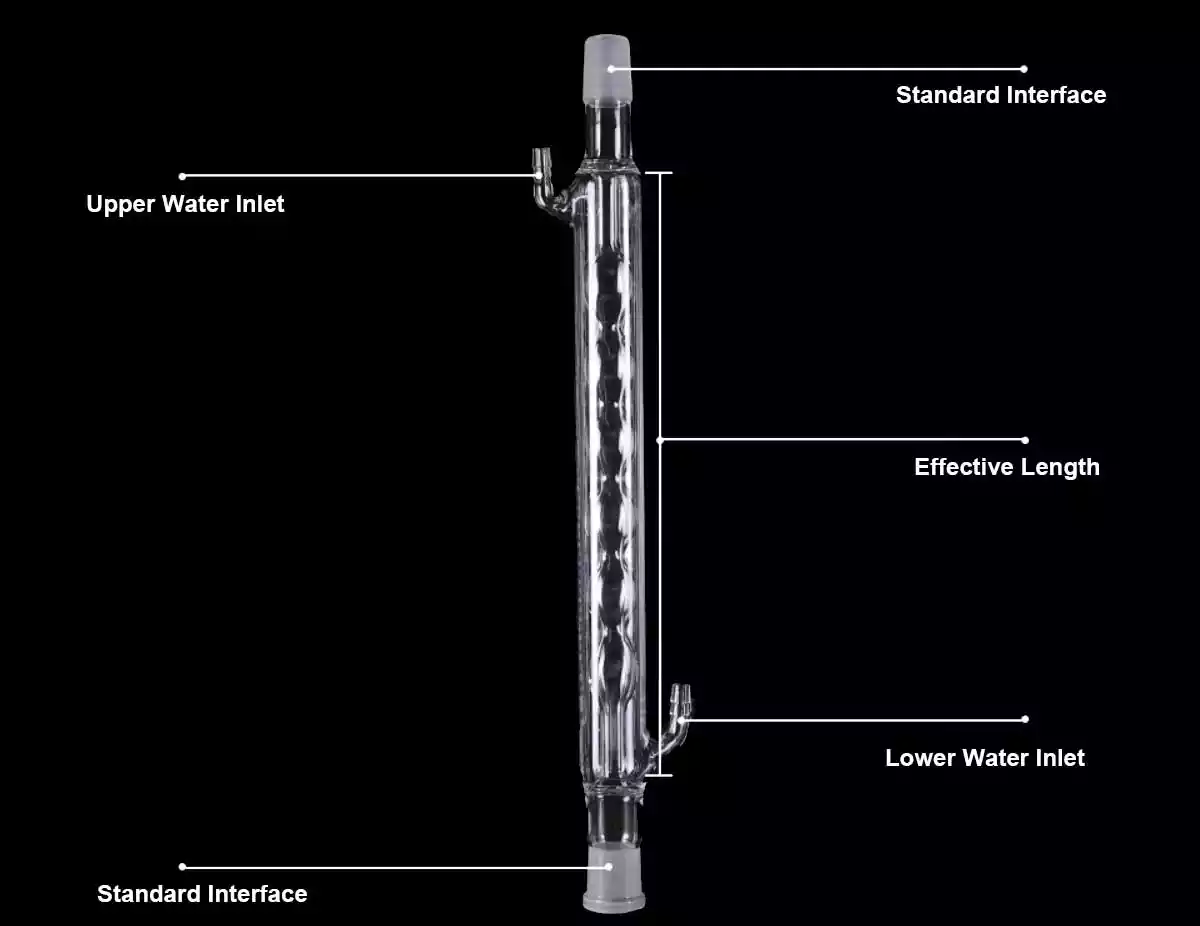
General Size Details of the Glass Condenser Tube:
Spiral shaped(effective length*interface size*interface size):
200mm*24*24/300mm*19*19/300mm*24*24/400mm*19*19/400mm*24*24/600mm*24*24
Straight shaped(effective length*interface size*interface size):
200mm*19*19/200mm*24*24/300mm*19*19/300mm*24*24/400mm*19*19/400mm*24*24/500mm*24*24
spherical shaped(effective length*interface size*interface size):
200mm*19*19/200mm*24*24/300mm*19*19/300mm*24*24/400mm*19*19/400mm*24*24/500mm*24*24/600mm*24*24
Also, accept customized sizes.
Application of the glass condenser tube:
When the steam temperature is more significant than 140 ℃, use an air-condensing pipe. When the temperature is less than 140 ℃, use a straight or bulb condenser tube. Note that bulb condenser tubes are generally used for reflux and cannot be used in distillation units.
Condenser tubes are usually used on flasks to be tested under reflux or distillation flasks to collect condensed liquid. The condensation of steam occurs on the inner wall of the inner tube. The space enclosed by the inner and outer lines is the water area, which absorbs the heat of the steam and removes the heat. There is usually high water pressure at the water inlet. The plastic pipe should be tied tightly with a tube bundle to prevent the water pipe from falling off. When used in the reflux state, a rubber stopper shall be inserted into the glass tube at the lower end of the condensing tube so that it can be inserted into the neck of the flask to receive the upward evaporated vapor in the flask.